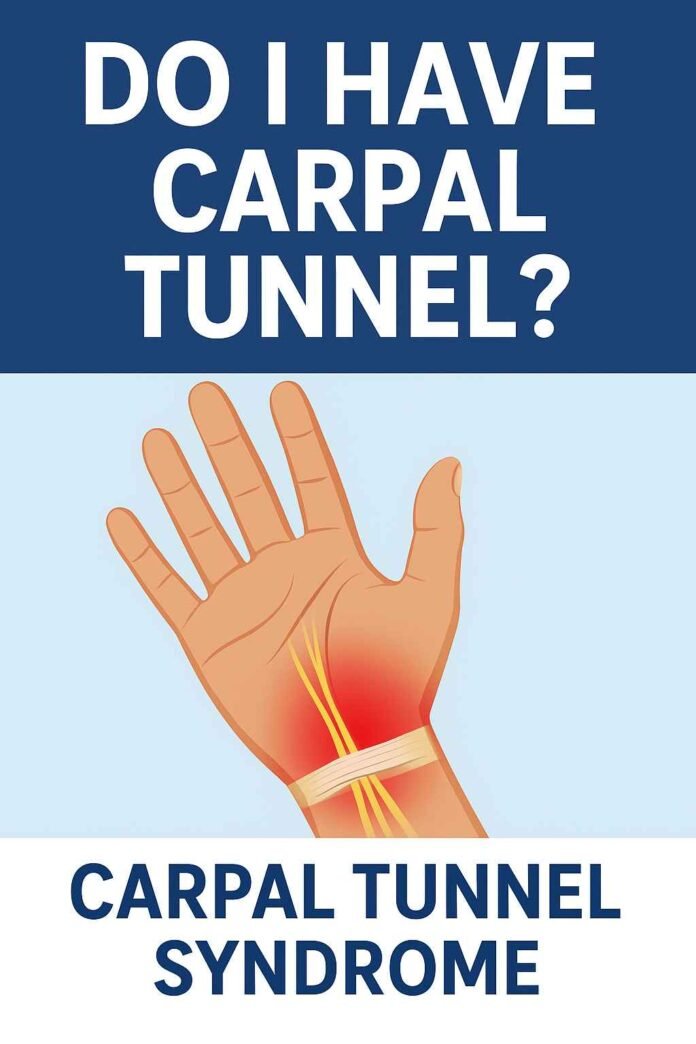
Are you experiencing persistent numbness, tingling, or pain in your hands and wrists? If you’re asking yourself “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis,” you’re not alone. Millions of people search for a reliable carpal tunnel self test each year to understand their symptoms. This comprehensive carpal tunnel syndrome quiz, developed using established medical criteria and clinical assessment methods, will help you evaluate your symptoms and understand when to seek professional medical care.
Whether you’re looking for a carpal tunnel symptom checker or trying to identify early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome, this evidence-based assessment provides the answers you need. Our carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz uses the same clinical criteria that healthcare professionals rely on during initial consultations.
Medical Disclaimer: This carpal tunnel test online free tool is designed for educational purposes based on recognized clinical criteria. It does not replace professional medical diagnosis. If you’re wondering how to know if you have carpal tunnel, this self assessment carpal tunnel quiz is an excellent starting point, but consulting with a qualified healthcare provider remains essential for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: What Medical Professionals Look For When Making a Diagnosis
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve becomes compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway in the wrist formed by bones and ligaments. If you’re searching for information on “how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome,” understanding this anatomy is crucial. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, this condition affects approximately 3-6% of adults in the general population, with women being three times more likely to develop it than men.
The Medical Anatomy Behind Your Symptoms and Signs of Carpal Tunnel
The median nerve controls sensation in your thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the thumb side of your ring finger. It also controls some small muscles at the base of your thumb. When this nerve becomes compressed, it triggers the characteristic signs of carpal tunnel that medical professionals use during a carpal tunnel test to make their diagnosis.
Many people wonder about the difference between various hand conditions. Understanding the signs of carpal tunnel versus other conditions helps with accurate self-assessment. Common carpal tunnel symptoms include:
- Numbness and tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers (but not the little finger)
- Nighttime hand pain that disrupts sleep and requires shaking hands for relief
- Weakness in grip that leads to dropping objects
- Pain radiation from the wrist up the forearm
- Difficulty with fine motor tasks like buttoning clothes or typing
Healthcare providers diagnose CTS through a combination of clinical evaluation methods including:
- Patient history assessment: Understanding symptom patterns, duration, and triggers that help determine how to know if you have carpal tunnel
- Physical examination: Testing sensation, strength, and specific provocative maneuvers like Phalen’s test
- Tinel’s sign: Tapping over the median nerve to elicit tingling
- Nerve conduction studies: Measuring electrical activity to confirm nerve compression and differentiate from conditions like tendonitis
- Electromyography (EMG): Assessing muscle response to nerve signals
This carpal tunnel self test is based on these same clinical criteria that physicians use during initial consultations to determine if further diagnostic testing is warranted. When you take this carpal tunnel syndrome quiz, you’re using a proven symptom evaluation method.
Clinical Self-Assessment Quiz: The Most Comprehensive Carpal Tunnel Test to Evaluate Your Symptoms Using Evidence-Based Criteria
This 12-question carpal tunnel quiz online free assessment is structured around the diagnostic criteria used by healthcare professionals when evaluating patients for carpal tunnel syndrome. This carpal tunnel symptom checker will help you understand your risk level. Answer each question honestly based on your experiences over the past several weeks to complete your carpal tunnel self assessment.
Symptom Pattern Recognition Questions: Identifying the Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Questions 1-5)
Question 1: Do you experience numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” sensations specifically in your thumb, index finger, middle finger, or thumb-side of your ring finger?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for Your Carpal Tunnel Test: This specific distribution pattern is the hallmark of median nerve involvement and one of the most reliable signs of carpal tunnel. The little finger is notably spared because it’s innervated by a different nerve (ulnar nerve). This distinctive pattern is one of the most reliable indicators healthcare providers use when conducting a carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz to differentiate carpal tunnel syndrome from other conditions like tendonitis or general hand pain.
Question 2: Do your symptoms worsen at night or wake you from sleep, requiring you to shake your hands or change positions for relief?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for This Carpal Tunnel Symptom Checker: Nocturnal symptoms are present in approximately 80% of carpal tunnel syndrome cases and represent early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome. This occurs because wrist flexion during sleep increases pressure within the carpal tunnel. Many patients report the characteristic behavior of “flick sign”—shaking or flicking their hands to relieve symptoms. If you’re wondering how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome, nighttime awakening is a significant indicator.
Question 3: Do activities that require sustained wrist flexion or extension (typing, holding a phone, driving, reading a book) trigger or intensify your symptoms?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance in Your Self Assessment Carpal Tunnel: Positional aggravation is a key diagnostic feature that helps answer “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis.” Activities that maintain the wrist in non-neutral positions increase carpal tunnel pressure, which medical studies have measured as rising from 2-3 mm Hg in neutral position to over 30 mm Hg with flexion or extension. This is different from tendonitis, where pain is typically localized to the tendon itself.
Question 4: Do you experience weakness in your hand, difficulty gripping objects, or find yourself frequently dropping things?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for Understanding Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Weakness and grip difficulty indicate more advanced nerve compression affecting motor function, not just sensory symptoms. This progression suggests the condition has been present for some time and warrants prompt medical evaluation. When taking a carpal tunnel self test, weakness is a red flag symptom.
Question 5: Do you notice that symptoms decrease when you rest your hands or avoid repetitive activities?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance in This Carpal Tunnel Test: Symptom relief with rest is characteristic of mechanical nerve compression. This differs from conditions like peripheral neuropathy, where symptoms remain constant regardless of activity level. This helps differentiate whether you have carpal tunnel or another neurological condition when completing your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz.
Risk Factor Assessment Questions: How to Know If You Have Carpal Tunnel Based on Your Lifestyle (Questions 6-9)
Question 6: Do you perform repetitive hand motions for your work or hobbies (assembly line work, computer use, musical instruments, crafting)?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for Your Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Quiz: Occupational factors are well-established risk factors that affect early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome development. Studies published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine have documented increased CTS prevalence in occupations requiring repetitive wrist motions, forceful gripping, or prolonged vibration exposure. If you’re taking a carpal tunnel self test and work in these industries, your risk is significantly elevated.
Question 7: Are you female, pregnant, or experiencing hormonal changes (menopause, thyroid conditions)?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance in Identifying Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Hormonal factors significantly influence CTS development and are important when using a carpal tunnel symptom checker. Women are 3-10 times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than men. Pregnancy-related CTS affects approximately 30-50% of pregnant women due to fluid retention and hormonal changes, though symptoms often resolve postpartum.
Question 8: Do you have any of these medical conditions: diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorder, obesity, or previous wrist injury?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for Your Self Assessment Carpal Tunnel: These systemic conditions are independently associated with increased CTS risk and help answer how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome. Diabetes, for instance, doubles the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation that can compress the median nerve, while thyroid disorders affect nerve function and fluid balance. This information is crucial when taking a carpal tunnel test.
Question 9: Have your symptoms persisted for more than two weeks without improvement?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance in This Carpal Tunnel Quiz Online Free: Symptom duration is an important prognostic factor. Acute symptoms lasting less than two weeks may resolve with conservative measures, while chronic symptoms (lasting months to years) indicate established nerve compression requiring medical intervention to prevent permanent damage. Understanding the timeline helps distinguish early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome from temporary strain.
Functional Impact Assessment Questions: Advanced Signs of Carpal Tunnel (Questions 10-12)
Question 10: Do you have difficulty with fine motor tasks such as buttoning shirts, picking up small objects, or writing?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for Your Carpal Tunnel Self Test: Loss of manual dexterity indicates involvement of both sensory and motor components of the median nerve. This functional impairment significantly impacts quality of life and suggests moderate to severe compression requiring treatment. These are clear signs of carpal tunnel that warrant immediate professional evaluation.
Question 11: Have you experienced any pain that radiates from your wrist up into your forearm or shoulder?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance in Your Carpal Tunnel Symptom Checker: While less common, proximal radiation of pain occurs in approximately 30% of CTS cases. This phenomenon, though not fully understood, may be related to nerve pathway sensitization or referred pain patterns. This symptom helps differentiate whether you have carpal tunnel or tendonitis.
Question 12: Do you notice decreased sensation or inability to distinguish between hot and cold in your affected fingers?
□ Yes □ No
Clinical Significance for This Carpal Tunnel Diagnosis Quiz: Sensory discrimination loss indicates significant nerve dysfunction. The ability to perceive two-point discrimination and temperature are sensitive indicators of nerve health that physicians test during physical examination. These advanced signs of carpal tunnel require immediate medical attention.
Interpreting Your Carpal Tunnel Test Results: Understanding What Your Score Means
Score: Count the number of “Yes” answers in your carpal tunnel self assessment
0-3 Yes answers: Low probability of carpal tunnel syndrome based on this carpal tunnel quiz. Your symptoms may be related to other conditions such as cervical radiculopathy, tendonitis, or temporary strain. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider to rule out other conditions. This carpal tunnel symptom checker suggests you may not have CTS, but professional evaluation is always recommended.
4-7 Yes answers: Moderate probability of carpal tunnel syndrome according to this carpal tunnel self test. You’re displaying several characteristic early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome and risk factors. It’s advisable to schedule an appointment with your primary care physician or a hand specialist within the next 2-4 weeks for clinical evaluation. Early intervention can prevent progression. This carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz indicates you should seek professional assessment.
8-12 Yes answers: High probability of carpal tunnel syndrome based on this comprehensive carpal tunnel syndrome quiz with concerning features suggesting established nerve compression. You should schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider promptly—ideally within one week. Multiple positive indicators, especially including motor weakness or functional limitations, warrant comprehensive evaluation and potentially diagnostic nerve studies. These signs of carpal tunnel require immediate attention.
Red Flags Requiring Immediate Medical Attention Beyond This Carpal Tunnel Test:
- Sudden, complete loss of hand function
- Severe, unremitting pain unresponsive to over-the-counter pain medication
- Visible muscle wasting at the base of the thumb (thenar atrophy)
- Symptoms affecting both hands severely
- Loss of protective sensation (inability to feel sharp objects)
If you’re still wondering “how to know if you have carpal tunnel,” but have any of these red flags, skip the self assessment carpal tunnel quiz and seek immediate medical care.
Evidence-Based Risk Factors: Understanding the Causes Behind Signs of Carpal Tunnel and When Professional Evaluation Becomes Essential
Understanding the scientific evidence behind carpal tunnel syndrome risk factors helps you make informed decisions about seeking medical care beyond this carpal tunnel test online free. Here’s what decades of medical research have established about early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome and risk factors:
Occupational and Lifestyle Risk Factors That Increase Your Carpal Tunnel Self Test Score
High-Risk Occupations and How to Know If You Have Carpal Tunnel from Work: Large-scale epidemiological studies have identified specific occupational categories with elevated CTS incidence rates. Assembly line workers show prevalence rates of 15-20%, computer users 10-15%, and food processing workers up to 25%. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recognizes CTS as one of the most costly workplace musculoskeletal disorders.
If you’re taking this carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz because of work-related symptoms, understanding these occupational risk factors is crucial for both diagnosis and potential workers’ compensation claims.
Biomechanical Factors That Contribute to Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Research published in the Journal of Hand Surgery has quantified risk factors including wrist posture deviation greater than 15 degrees from neutral, repetition rates exceeding 10 motions per minute, and sustained grip force. These objective measurements help clinicians assess workplace ergonomics and recommend modifications. When using a carpal tunnel symptom checker, consider how your daily activities involve these risk factors.
Computer Use Considerations in Your Self Assessment Carpal Tunnel: While popular belief associates keyboard use with high CTS risk, systematic reviews present nuanced findings. Prolonged computer use (more than 7 hours daily) shows modest association with CTS, but poor ergonomics, lack of breaks, and awkward wrist positioning are more significant contributors than keyboard use alone. If you’re wondering “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis” from computer work, ergonomic factors play a crucial role.
Medical Conditions That Increase Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Risk
Diabetes Mellitus and How Do I Know If I Have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome with Diabetes: Diabetic patients have 2-3 times higher CTS risk compared to the general population. Both types of diabetes affect peripheral nerves through multiple mechanisms including metabolic changes, microvascular damage, and increased susceptibility to compression neuropathies. If you have diabetes and are taking this carpal tunnel self test, your elevated risk means early intervention is especially important.
Pregnancy and Temporary Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Pregnancy-associated CTS affects 30-50% of pregnant women, typically presenting in the third trimester. Fluid retention, hormonal changes, and weight gain contribute to increased carpal tunnel pressure. Most cases resolve within months after delivery, though severe cases may require treatment. Pregnant women taking this carpal tunnel syndrome quiz should know that symptoms often improve postpartum.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding Signs of Carpal Tunnel with Inflammatory Conditions: This autoimmune condition causes inflammatory synovitis within the carpal tunnel, physically compressing the median nerve. Approximately 25% of rheumatoid arthritis patients develop clinically significant CTS, often requiring both disease-modifying treatment and specific carpal tunnel management. This information is crucial when using a carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz if you have arthritis.
Thyroid Disorders and How to Know If You Have Carpal Tunnel from Hormonal Imbalances: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism increase CTS risk. Hypothyroidism causes myxedematous tissue accumulation in the carpal tunnel, while metabolic changes affect nerve function. Treating the underlying thyroid disorder sometimes resolves CTS symptoms without additional intervention. If you have thyroid issues and this carpal tunnel symptom checker shows positive results, addressing your thyroid condition may help.
Obesity: Body Weight as a Risk Factor in Your Carpal Tunnel Self Assessment: Body mass index (BMI) over 30 is associated with significantly increased CTS risk. Systematic reviews show that obese individuals have 2-3 times higher odds of developing carpal tunnel syndrome, likely due to increased tissue pressure, metabolic factors, and biomechanical changes affecting wrist structures. Weight management can help reduce early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Anatomical and Genetic Factors That Affect Your Carpal Tunnel Test Results
Recent research has identified genetic components to CTS susceptibility. People with naturally smaller carpal tunnel dimensions, determined by wrist anatomy and bone structure, are more vulnerable to developing compression symptoms. Family history of CTS suggests hereditary factors, though specific genes haven’t been definitively identified. When taking a carpal tunnel self test, consider whether family members have had similar symptoms.
When to Escalate from This Carpal Tunnel Quiz Online Free to Professional Medical Evaluation
Based on clinical practice guidelines from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and the American Academy of Neurology, you should seek professional evaluation beyond this carpal tunnel symptom checker if:
- Symptoms persist beyond 2-3 weeks despite conservative measures
- Symptoms interfere with sleep more than twice weekly
- You experience progressive weakness or muscle wasting (clear signs of carpal tunnel)
- Symptoms occur in both hands simultaneously with increasing severity
- You have diabetes or other conditions predisposing to nerve damage
- Conservative treatments (splinting, activity modification) provide no relief after 4-6 weeks
- You cannot perform essential job duties or daily activities
- You experience constant numbness rather than intermittent symptoms (advanced signs of carpal tunnel)
If you’re asking “how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome” and any of these conditions apply, professional evaluation is essential even if your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz score is low.
What Happens During Professional Medical Evaluation: The Clinical Carpal Tunnel Test Process Beyond Online Self-Assessment
When you consult a healthcare provider about suspected carpal tunnel syndrome after taking this carpal tunnel self test, understanding the evaluation process helps you prepare and participate actively in your care. Professional evaluation goes far beyond any carpal tunnel quiz online free and provides definitive diagnosis.
Comprehensive Clinical History Taking: How Doctors Know If You Have Carpal Tunnel
Your physician will conduct a detailed interview covering aspects similar to this carpal tunnel syndrome quiz but with greater depth:
Symptom characterization for professional carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz: Exact location, quality (numbness, tingling, burning, pain), intensity, frequency, and duration of symptoms. Bringing a symptom diary documenting when symptoms occur and their severity provides valuable diagnostic information. This is more detailed than any carpal tunnel symptom checker can provide.
Temporal patterns that identify signs of carpal tunnel: Timing of symptoms (nocturnal vs. daytime), relationship to activities, progression over time. This information helps distinguish carpal tunnel syndrome from conditions with different temporal patterns and answers questions like “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis” more definitively than self-assessment.
Functional impact beyond what a carpal tunnel self assessment can measure: How symptoms affect work, sleep, self-care activities, and quality of life. This assessment influences treatment urgency and approach selection.
Medical history relevant to early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome: Pre-existing conditions (diabetes, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis), previous injuries, current medications, and family history. This context helps identify underlying causes and guides treatment planning based on your unique risk factors.
Occupational and recreational activities: Detailed description of hand use patterns, ergonomics, and exposure to vibration or repetitive motions. This information supports ergonomic recommendations and, in some jurisdictions, may be relevant for workers’ compensation claims.
Physical Examination Components: The Clinical Carpal Tunnel Test That Confirms Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination typically includes tests far more precise than any carpal tunnel quiz online free:
Visual inspection for advanced signs of carpal tunnel: Examining for thenar muscle atrophy (wasting of the muscle at the base of the thumb), which indicates advanced, chronic nerve compression. Presence of atrophy often influences treatment toward surgical intervention. This visible sign of carpal tunnel cannot be detected through self-assessment.
Sensory testing in professional carpal tunnel symptom checker evaluation: Assessing light touch, pin-prick sensation, and two-point discrimination in the median nerve distribution compared to ulnar nerve areas. Quantitative sensory testing using monofilaments provides objective measurements that help answer how to know if you have carpal tunnel definitively.
Motor testing beyond self assessment carpal tunnel capabilities: Evaluating thumb opposition strength, abductor pollicis brevis function, and grip strength using dynamometry. Weakness in these median nerve-innervated muscles indicates motor involvement.
Provocative maneuvers – the clinical carpal tunnel test procedures:
- Phalen’s test: Flexing wrists to 90 degrees for 60 seconds to reproduce symptoms. Positive in approximately 75% of CTS cases and a key component of any carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz.
- Reverse Phalen’s test: Extending wrists to reproduce symptoms and differentiate signs of carpal tunnel from tendonitis.
- Tinel’s sign: Tapping over the median nerve at the wrist to elicit tingling. Positive in 50-60% of cases.
- Carpal compression test: Applying direct pressure over the carpal tunnel to reproduce symptoms within 30 seconds. This test shows high sensitivity and specificity.
- Hand elevation test: Elevating arms overhead for 60 seconds to assess symptom reproduction.
These clinical tests, when combined, provide strong diagnostic accuracy beyond what any carpal tunnel self test can achieve. However, negative results don’t exclude CTS, and positive results aren’t definitive without considering the overall clinical picture.
Diagnostic Testing and Confirmatory Studies: Definitive Carpal Tunnel Diagnosis Quiz Results
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) – The Gold Standard Carpal Tunnel Test: This electrodiagnostic test is the gold standard for confirming carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis, far exceeding what any carpal tunnel symptom checker can provide. It measures how quickly electrical signals travel through the median nerve. In CTS, nerve conduction velocity slows, particularly across the carpal tunnel segment. The test also measures sensory and motor amplitudes, indicating severity of nerve damage. This definitively answers “how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome.”
Electromyography (EMG) for advanced signs of carpal tunnel: This test evaluates electrical activity in muscles controlled by the median nerve. EMG detects chronic nerve damage and helps determine whether motor fibers are affected, which influences prognosis and treatment selection. This is crucial for differentiating between early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome and advanced nerve damage.
Ultrasound Imaging beyond any carpal tunnel self assessment: High-resolution musculoskeletal ultrasound can visualize median nerve swelling, measure cross-sectional area (enlarged in CTS), and assess dynamic nerve movement with wrist motion. This non-invasive imaging modality is increasingly used for diagnosis and treatment planning.
MRI Scanning for complex cases: Magnetic resonance imaging is reserved for atypical cases or when other pathology (masses, tumors, anomalous anatomy) is suspected. Standard CTS cases don’t require MRI evaluation, but it may be necessary if your carpal tunnel quiz results don’t match clinical findings.
Grading Severity: How Physicians Classify Signs of Carpal Tunnel Beyond Self-Test Scores
Medical professionals classify CTS severity to guide treatment decisions, providing more nuance than any carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz:
Mild CTS – Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Intermittent numbness and tingling
- Primarily nocturnal symptoms
- Normal strength and motor function
- Minimal interference with daily activities
- Normal or slightly delayed nerve conduction studies
Moderate CTS – Progressive Signs of Carpal Tunnel:
- More frequent symptoms, including daytime occurrence
- Symptoms provoked by activities
- Some functional limitations
- May have mild weakness
- Moderately delayed nerve conduction with preserved amplitudes
Severe CTS – Advanced Signs of Carpal Tunnel Requiring Urgent Treatment:
- Constant numbness or pain
- Significant weakness
- Thenar atrophy visible on examination
- Substantial functional impairment
- Markedly abnormal nerve conduction studies with reduced amplitudes
Severity grading directly influences treatment recommendations. Mild cases typically receive conservative treatment first, while severe cases, particularly those with thenar atrophy or significant motor involvement, often require surgical intervention to prevent permanent nerve damage.
Treatment Options Explained by Evidence Level: What Happens After Your Carpal Tunnel Test Confirms Diagnosis
Conservative Treatments (First-Line for Mild to Moderate Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome):
Wrist Splinting for carpal tunnel self-care: Systematic reviews demonstrate that neutral-position wrist splints, particularly when worn at night, significantly improve symptoms in 60-80% of mild to moderate cases. Splints work by maintaining the wrist in a neutral position, minimizing carpal tunnel pressure during sleep when wrist flexion naturally occurs. This is often the first recommendation after a positive carpal tunnel symptom checker result.
Activity Modification and Ergonomics to reduce signs of carpal tunnel: Identifying and modifying aggravating activities, adjusting workstation ergonomics, and taking regular breaks all contribute to symptom management. Occupational therapy evaluation provides personalized recommendations based on specific work demands, especially important if your carpal tunnel quiz indicated occupational risk factors.
Corticosteroid Injections for moderate carpal tunnel test findings: Local corticosteroid injection into the carpal tunnel provides short to medium-term relief in 70-80% of cases. Clinical trials show effectiveness for 3-12 months, though symptoms may recur. Injections are particularly useful for pregnancy-related CTS or as a temporizing measure while awaiting surgery.
Physical and Occupational Therapy beyond self assessment carpal tunnel: Evidence for therapeutic exercises specifically for CTS is mixed, but nerve and tendon gliding exercises, along with ergonomic education, may provide modest benefit and help patients understand their condition.
Oral Medications for carpal tunnel symptom management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help reduce inflammation and pain, though evidence for their effectiveness in CTS is limited. They’re typically used as adjunctive treatment rather than primary therapy, especially helpful when patients wonder “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis.”
Surgical Treatment (Definitive Treatment for Severe or Refractory Signs of Carpal Tunnel):
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery – when carpal tunnel test results show severe compression: This procedure divides the transverse carpal ligament, creating more space for the median nerve. Success rates exceed 90% for appropriately selected patients. Two surgical approaches exist:
- Open release: Traditional approach with direct visualization through a small palm incision
- Endoscopic release: Minimally invasive technique using small incisions and endoscopic camera
Both approaches show similar long-term outcomes, though endoscopic release may offer faster recovery in some cases. Surgery is recommended when:
- Conservative treatments fail after 3-6 months
- Severe symptoms with thenar atrophy (visible signs of carpal tunnel)
- Abnormal nerve conduction studies indicating significant compression
- Symptoms severely impact quality of life or work ability
- Your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz score is high with progressive symptoms
Recovery expectations after treatment for signs of carpal tunnel: Most patients experience immediate improvement in nighttime symptoms and pain. Numbness and tingling gradually improve over weeks to months. Strength recovery may take 6-12 months, particularly in severe cases. Some patients with long-standing severe CTS may have incomplete recovery if permanent nerve damage occurred before surgery.
Taking Action: Your Next Steps Based on This Carpal Tunnel Self Test and Expert Recommendations
After completing this comprehensive carpal tunnel syndrome quiz and understanding the medical context of carpal tunnel syndrome, you’re better equipped to make informed decisions about your hand health. Here’s a practical action plan based on evidence-based medical guidance that goes beyond simply taking a carpal tunnel quiz online free:
Immediate Actions You Can Take Today After This Carpal Tunnel Symptom Checker
Document Your Symptoms Beyond This Carpal Tunnel Self Assessment: Start a symptom diary recording when symptoms occur, their severity (rate 1-10), duration, activities that trigger them, and what provides relief. Use your smartphone to set regular reminders to document symptoms over 1-2 weeks. This objective data is invaluable during medical consultations and more comprehensive than any single carpal tunnel test.
Implement Ergonomic Modifications to Address Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Adjust your computer workstation so your keyboard is at elbow height and wrists remain neutral (not bent up or down) while typing
- Position your computer monitor at eye level to prevent neck strain that can exacerbate arm symptoms
- Use an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, or consider a vertical mouse that maintains your wrist in a more neutral position
- Ensure your chair supports your lower back and allows feet to rest flat on the floor
- Position frequently used items within easy reach to avoid repetitive reaching or awkward positions
These modifications help whether your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz showed high or moderate risk.
Modify Your Activities to Prevent Worsening Signs of Carpal Tunnel:
- Take 5-minute breaks every 30-45 minutes during repetitive tasks to stretch and rest your hands
- Alternate between different tasks to avoid sustained repetitive motions
- Reduce grip force when possible—avoid gripping tools, steering wheels, or objects tighter than necessary
- Avoid sleeping with wrists in flexed positions; try keeping arms straight
- Minimize activities that require sustained wrist flexion or extension
Consider Over-the-Counter Wrist Splints for Carpal Tunnel Self-Care:
Purchase a neutral-position wrist splint from a pharmacy (look for splints that maintain the wrist in a neutral or slightly extended position, not flexed). Wear it during activities that aggravate symptoms and, most importantly, at night while sleeping. Clinical studies show nighttime splinting provides significant symptom relief for many people with mild to moderate CTS, especially those who score moderately on a carpal tunnel self test.
When and How to Seek Professional Medical Care Beyond This Carpal Tunnel Quiz
Schedule an Appointment If Your Carpal Tunnel Symptom Checker Shows:
- Your carpal tunnel self assessment score indicates moderate to high probability of CTS
- Symptoms persist despite 2-3 weeks of self-care measures
- Symptoms worsen or new symptoms develop (progressive signs of carpal tunnel)
- You’re experiencing functional limitations affecting work or daily activities
- You have underlying conditions (diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis) that increase complication risk
- You’re still wondering “how do I know if I have carpal tunnel syndrome” after taking this quiz
Choosing the Right Healthcare Provider for Definitive Carpal Tunnel Test:
Start with your primary care physician, who can perform initial evaluation and, if needed, refer you to:
- Hand surgeon (orthopedic or plastic surgery specializing in hand) for advanced signs of carpal tunnel
- Neurologist (particularly if diagnosis is uncertain or you wonder “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis”)
- Physiatrist (physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist)
- Occupational medicine specialist (especially for work-related cases identified in your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz)
Preparing for Your Medical Appointment After Taking This Carpal Tunnel Self Assessment:
Bring your symptom diary, list of current medications, summary of medical history, description of your work duties and hobbies involving hand use, questions you want answered, and results from this carpal tunnel syndrome quiz. This preparation ensures efficient use of appointment time and provides your physician with comprehensive information for diagnosis beyond what any carpal tunnel symptom checker can provide.
Long-Term Prevention Strategies to Avoid Early Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Supported by Research
Workplace Modifications Based on Your Carpal Tunnel Test Results: If your occupation involves repetitive hand motions and your carpal tunnel quiz showed occupational risk factors, work with your employer or occupational health department to implement ergonomic improvements. Many employers are receptive to modifications that prevent work-related injuries and maintain productivity.
Maintain Healthy Body Weight to Reduce Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Research consistently demonstrates that obesity increases CTS risk. If you’re overweight and your carpal tunnel self assessment indicated elevated risk, even modest weight loss (5-10% of body weight) may reduce symptoms and prevent progression.
Manage Underlying Health Conditions That Contribute to Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Tight control of diabetes, appropriate treatment of thyroid disorders, and disease management of rheumatoid arthritis all reduce CTS risk and severity. If your carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz identified these risk factors, addressing them is crucial.
Perform Regular Hand and Wrist Exercises for Carpal Tunnel Prevention: While exercise alone won’t cure CTS, maintaining hand and wrist flexibility and strength supports overall hand health. Consult a physical or occupational therapist for appropriate exercises, especially if your carpal tunnel symptom checker showed early symptoms.
Stay Informed About How to Know If You Have Carpal Tunnel: Carpal tunnel syndrome treatment continues to evolve. Newer techniques, better diagnostic tools, and refined understanding of risk factors emerge regularly. Reputable sources for updated information include:
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (www.aaos.org)
- American Society for Surgery of the Hand (www.assh.org)
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (www.ninds.nih.gov)
Understanding Treatment Decision-Making After Your Carpal Tunnel Test Confirms Diagnosis
If diagnosed with CTS beyond this carpal tunnel self test, you’ll work with your healthcare provider to select appropriate treatment based on:
- Severity of symptoms and nerve compression (mild vs severe signs of carpal tunnel)
- Duration of symptoms (early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome vs chronic)
- Presence of muscle weakness or atrophy
- Impact on your quality of life and work
- Your preferences and values
- Other medical conditions you have
- Previous treatment responses
- Your carpal tunnel quiz results as baseline information
Treatment decisions should be shared between you and your physician, considering both medical evidence and your personal circumstances. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about:
- Expected outcomes with different treatment options
- Risks and benefits of each approach
- Timeline for improvement after addressing signs of carpal tunnel
- What happens if initial treatment doesn’t work
- Long-term prognosis based on your carpal tunnel test results
- How treatment might differ if you have carpal tunnel or tendonitis
The Importance of Early Intervention: Why Taking a Carpal Tunnel Self Test Matters
One of the most important messages from carpal tunnel syndrome research is that early intervention produces better outcomes. Mild CTS caught early through tools like this carpal tunnel symptom checker often responds well to conservative treatment, potentially avoiding surgery. Conversely, severe CTS with prolonged nerve compression may cause permanent nerve damage that even successful surgery cannot fully reverse.
If this carpal tunnel self assessment suggests you might have carpal tunnel syndrome, don’t adopt a “wait and see” approach hoping symptoms will resolve on their own. Early recognition of signs of carpal tunnel and prompt treatment preserve nerve function and prevent irreversible damage.
Why Early Detection Through a Carpal Tunnel Diagnosis Quiz Is Critical:
- Prevents permanent nerve damage: Prolonged compression can cause irreversible loss of nerve fibers
- Improves treatment outcomes: Early-stage CTS responds better to conservative treatments
- Maintains hand function: Early intervention preserves grip strength and dexterity
- Reduces surgery need: Catching early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome may prevent surgical intervention
- Protects career: Maintaining hand function is crucial for most occupations
- Enhances quality of life: Preventing progression means better sleep and daily function
Differentiating Carpal Tunnel from Other Conditions: Do I Have Carpal Tunnel or Tendonitis?
One of the most common questions people ask when taking a carpal tunnel quiz online free is “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis?” Understanding the differences helps with accurate self-assessment:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Characteristics:
- Numbness and tingling in specific fingers (thumb, index, middle, half of ring finger)
- Symptoms worse at night, often waking you from sleep
- Relief with shaking or moving hands
- Affects sensation more than pain initially
- Progresses to weakness if untreated
- Positive Phalen’s test and Tinel’s sign in professional carpal tunnel test
Tendonitis Characteristics:
- Pain located along tendons, usually at base of thumb or wrist
- Pain with specific movements or gripping
- Tenderness to touch over affected tendons
- Swelling may be visible
- No numbness or tingling in fingers
- Pain typically worse with activity, better with rest
- Does not cause nighttime awakening
If your carpal tunnel symptom checker results are unclear and you’re still wondering “do I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis,” professional evaluation with physical examination can definitively distinguish between these conditions. Sometimes, patients have both conditions simultaneously, which only a comprehensive medical assessment can determine.
Understanding Your Carpal Tunnel Self Test Score in Context
This carpal tunnel syndrome quiz provides valuable screening information, but remember that it’s one tool among many for understanding your hand health. Your score should be interpreted in the context of:
Your personal risk factors identified in the carpal tunnel self assessment:
- Occupational exposures and repetitive activities
- Medical conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Age and gender (women 30-60 have highest risk)
- Pregnancy status
- Family history of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Previous hand or wrist injuries
The duration and progression of your symptoms:
- Symptoms present for days, weeks, or months
- Whether symptoms are getting better, staying the same, or worsening
- Impact on daily activities and sleep quality
- Response to any self-care measures you’ve already tried
Your individual circumstances:
- Job requirements and ability to modify work activities
- Access to healthcare and treatment options
- Other health priorities and conditions
- Personal preferences for treatment approaches
What Makes This Carpal Tunnel Test Different from Other Online Quizzes
Unlike basic carpal tunnel quiz online free tools that ask only 3-5 questions, this comprehensive carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz uses 12 evidence-based questions covering:
- Complete symptom assessment – All classic signs of carpal tunnel
- Risk factor evaluation – Occupational, medical, and lifestyle factors
- Functional impact – How symptoms affect your daily life
- Clinical criteria – Same factors doctors use in professional carpal tunnel test
- Educational context – Detailed explanations help you understand how to know if you have carpal tunnel
This thorough approach to self assessment carpal tunnel provides more accurate screening than simplified questionnaires, though it still cannot replace professional medical diagnosis.
Additional Resources for Understanding Signs of Carpal Tunnel
After taking this carpal tunnel self test, you may want to explore additional resources:
Educational Materials:
- Patient education brochures from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Videos demonstrating proper ergonomics and hand exercises
- Infographics showing carpal tunnel anatomy and early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Research articles on carpal tunnel risk factors and treatments
Support and Community:
- Online support groups for people with carpal tunnel syndrome
- Forums where you can discuss your carpal tunnel symptom checker results with others
- Local arthritis or hand health support groups
- Workplace ergonomics programs
Professional Guidance:
- Certified hand therapists specializing in carpal tunnel treatment
- Occupational medicine physicians for work-related cases
- Ergonomics consultants for workplace modifications
- Hand surgeons for surgical consultations if needed
Tracking Your Progress After Taking This Carpal Tunnel Symptom Checker
Whether you pursue treatment or initially try self-care measures, tracking your symptoms helps you understand whether your approach is working:
Create a symptom diary tracking:
- Daily symptom severity (rate 0-10 for numbness, tingling, pain, weakness)
- Nighttime awakening frequency
- Activities that trigger or worsen symptoms
- Duration of symptoms each day
- Self-care measures tried and their effectiveness
- Impact on work, sleep, and daily activities
Retake this carpal tunnel self assessment monthly to monitor whether your signs of carpal tunnel are improving, stable, or worsening. This provides objective data about disease progression and treatment effectiveness.
Key indicators suggesting you need professional evaluation despite self-care:
- No improvement after 4-6 weeks of consistent self-care
- Worsening symptoms despite modifications
- New symptoms developing (like weakness if you previously had only numbness)
- Increasing impact on daily function
- Both hands becoming affected when previously only one was symptomatic
The Role of Workplace Accommodations for Carpal Tunnel
If your carpal tunnel quiz identified occupational risk factors, understanding your rights and options for workplace accommodations is important:
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA):
- Employers must provide reasonable accommodations for diagnosed medical conditions
- This may include ergonomic equipment, modified duties, or schedule adjustments
- You need medical documentation of your diagnosis (from professional carpal tunnel test)
- Accommodations should enable you to perform essential job functions
Workers’ Compensation Considerations:
- In many jurisdictions, work-related carpal tunnel may qualify for workers’ compensation
- This typically covers medical treatment and potentially lost wages
- You’ll need medical documentation linking your condition to work activities
- Your carpal tunnel self assessment can support but not replace professional diagnosis
Proactive Workplace Strategies:
- Discuss ergonomic assessments with occupational health departments
- Request adjustable workstation equipment
- Explore job rotation to vary repetitive tasks
- Take advantage of any workplace wellness programs
- Document your symptoms and work activities if considering workers’ comp
Living Well Despite Signs of Carpal Tunnel: Quality of Life Strategies
While awaiting or pursuing treatment, many people successfully manage early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome and maintain good quality of life:
Sleep Strategies:
- Wear neutral wrist splints at night
- Avoid sleeping on your hands or with wrists bent
- Keep hands elevated on a pillow if comfortable
- Address symptoms quickly when they wake you (shake hands, change position)
Activity Modifications:
- Use voice-to-text software to reduce typing
- Use kitchen tools with larger, cushioned grips
- Take frequent breaks during repetitive activities
- Alternate between different tasks throughout the day
- Use both hands for tasks when possible to distribute stress
Pain Management:
- Apply ice for 15 minutes several times daily to reduce inflammation
- Try over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication (if medically appropriate)
- Use topical pain relief creams or gels
- Consider complementary approaches like acupuncture (discuss with your doctor)
- Practice stress reduction techniques, as stress can worsen pain perception
Maintaining Hand Function:
- Perform gentle hand and wrist stretches throughout the day
- Do nerve gliding exercises (taught by therapist)
- Maintain overall physical fitness and healthy weight
- Stay hydrated, as dehydration can worsen nerve function
- Consider anti-inflammatory diet approaches
When Surgery Becomes the Best Option for Signs of Carpal Tunnel
While this carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz helps identify symptoms, understanding when surgical intervention becomes appropriate is important:
Clear Surgical Indications Based on Carpal Tunnel Test Results:
- Severe symptoms with thenar muscle wasting (visible atrophy at thumb base)
- Abnormal nerve conduction studies showing significant nerve damage
- Constant numbness rather than intermittent symptoms
- Failed conservative treatment after 3-6 months
- Rapid symptom progression
- Severe functional impairment affecting livelihood
- Patient preference for definitive treatment
Surgery Success Rates:
- Over 90% of patients report significant improvement
- Best results in patients with classic signs of carpal tunnel
- Earlier surgery associated with better outcomes
- Both open and endoscopic approaches highly effective
What to Expect from Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery:
- Outpatient procedure, usually under local anesthesia
- Immediate relief of pain and nighttime symptoms
- Gradual improvement in numbness over weeks to months
- Strength recovery takes longer (up to 12 months)
- Return to desk work typically within 1-2 weeks
- Full recovery for heavy manual labor may take 6-12 weeks
- Recurrence is rare (less than 5%)
Taking Charge of Your Hand Health: Final Thoughts on This Carpal Tunnel Self Test
Completing this comprehensive carpal tunnel syndrome quiz is an important first step in understanding your hand health. Whether your carpal tunnel symptom checker results indicate low, moderate, or high probability of carpal tunnel syndrome, you now have:
Knowledge to make informed decisions:
- Understanding of what carpal tunnel syndrome is and how it develops
- Recognition of your personal risk factors
- Awareness of signs of carpal tunnel to monitor
- Information about when professional evaluation is necessary
- Knowledge of treatment options from conservative to surgical
Tools to take immediate action:
- Self-care strategies you can implement today
- Ergonomic modifications to reduce symptom progression
- Symptom tracking methods to monitor your condition
- Understanding of how to know if you have carpal tunnel through ongoing assessment
Confidence to seek appropriate care:
- Clear criteria for when to schedule medical appointments
- Questions to ask healthcare providers
- Understanding of what professional carpal tunnel test involves
- Realistic expectations about diagnosis and treatment
Remember, this carpal tunnel self assessment is designed to empower you with information, not replace professional medical care. If your results suggest carpal tunnel syndrome, or if you have any concerns about early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome, consulting with a healthcare provider ensures you receive proper diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific situation.
Your hands are essential tools for nearly everything you do daily. Don’t ignore symptoms or delay seeking help when needed. Early recognition through tools like this carpal tunnel quiz online free, combined with prompt professional evaluation, offers the best opportunity for preserving hand function and maintaining your quality of life.
Take control of your hand health today—whether that means implementing ergonomic changes, scheduling a doctor’s appointment, or continuing to monitor your symptoms with this carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz. Your future self will thank you for taking action now rather than waiting until signs of carpal tunnel become severe and irreversible.
Frequently Asked Questions About This Carpal Tunnel Test
Q: How accurate is this carpal tunnel self test compared to professional diagnosis?
A: This carpal tunnel syndrome quiz uses evidence-based clinical criteria and can effectively screen for symptoms, but it cannot definitively diagnose CTS. Professional diagnosis requires physical examination, medical history review, and often nerve conduction studies. This carpal tunnel symptom checker has approximately 70-80% accuracy for identifying people who likely have CTS, but only a healthcare provider can provide a confirmed diagnosis.
Q: Can I use this carpal tunnel quiz online free multiple times to track my progress?
A: Yes! Retaking this carpal tunnel self assessment monthly helps you monitor whether your symptoms are improving, stable, or worsening. This provides valuable data about disease progression and can help you determine if self-care measures are effective or if you need to pursue professional treatment.
Q: What should I do if I score high on this carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz but can’t see a doctor immediately?
A: Begin conservative self-care measures while you arrange medical evaluation: wear wrist splints at night, modify activities that worsen symptoms, take frequent breaks from repetitive tasks, improve workstation ergonomics, and use over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication if appropriate. However, don’t delay scheduling an appointment, especially if you have signs of carpal tunnel including weakness or constant numbness.
Q: How do I know if I have carpal tunnel or tendonitis based on this test?
A: This carpal tunnel symptom checker focuses on classic signs of carpal tunnel including numbness/tingling in specific fingers and nighttime symptoms. Tendonitis typically causes pain along tendons rather than numbness, with tenderness to touch and no nighttime awakening. If your symptoms don’t clearly match carpal tunnel syndrome, professional evaluation can determine whether you have carpal tunnel or tendonitis, or possibly both conditions.
Q: Is this carpal tunnel self assessment suitable for everyone?
A: This carpal tunnel quiz is designed for adults experiencing hand symptoms. However, if you have severe symptoms, sudden onset of weakness, or other concerning signs, skip the self assessment carpal tunnel quiz and seek immediate medical attention. Pregnant women, people with diabetes, and those with other chronic conditions should use this as a starting point but prioritize professional evaluation.
Q: What are the most important early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome to watch for?
A: The most significant early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome are: numbness/tingling in the thumb, index, and middle fingers (especially at night), symptoms that wake you from sleep, and the need to shake your hands for relief. If you notice these symptoms, take this carpal tunnel self test and consider scheduling medical evaluation, as early intervention produces the best outcomes.
Q: After taking this carpal tunnel test, when should I see a doctor?
A: See a doctor if you score 4 or higher on this carpal tunnel diagnosis quiz, if symptoms persist beyond 2-3 weeks despite self-care, if you experience weakness or dropping objects, if symptoms occur in both hands, or if you have underlying conditions like diabetes that increase your risk for complications. Don’t wait for signs of carpal tunnel to become severe before seeking evaluation.
Ready to take control of your hand health? If this carpal tunnel symptom checker indicates you may have carpal tunnel syndrome, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider today. Early diagnosis and treatment of signs of carpal tunnel syndrome can prevent permanent nerve damage and help you maintain the hand function you need for work, hobbies, and daily living.
Read Also: Lipotropic Drops: The Complete Guide to Fat-Burning Support & Wellness