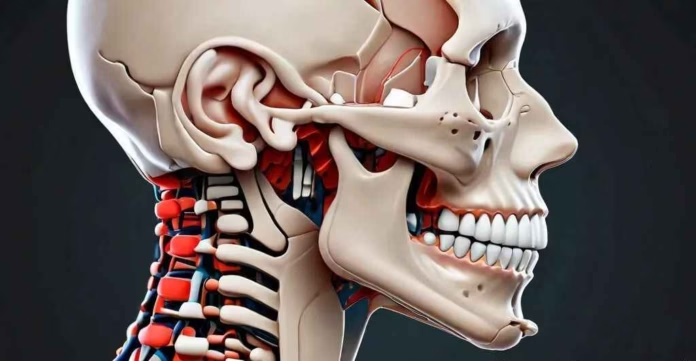
In this blog post, we’ll explore the connection between TMJ and these seemingly unrelated symptoms, and discuss what you can do to find relief and also try to answer the question Can TMJ Cause Waking Up with Ear Fullness and Dizziness?.
Temporomandibular joint disorder, or TMJ, is a common condition that affects the jaw joint and the surrounding muscles. While the primary symptoms of TMJ are often jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty chewing, many people with this condition also experience other, less obvious symptoms, such as ear fullness and dizziness.
Table of Contents
What is TMJ?
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the joint that connects your jaw to your skull. It’s a complex joint that allows for the smooth, coordinated movement of your jaw as you speak, chew, and yawn. When this joint becomes injured, inflamed, or misaligned, it can lead to a condition known as temporomandibular joint disorder, or TMJ.TMJ can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Injury or trauma to the jaw
- Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism)
- Stress and anxiety
- Arthritis
- Structural problems with the jaw joint
The most common symptoms of TMJ include:
- Pain or tenderness in the jaw, face, or neck
- Difficulty opening the mouth wide
- Clicking, popping, or grinding sounds in the jaw
- Headaches, especially around the temples
- Earaches or a feeling of fullness in the ears
How Can TMJ Cause waking up with Ear Fullness and Dizziness?
While the connection between TMJ and ear fullness or dizziness may not be immediately obvious, there are several reasons why these symptoms can occur in people with TMJ.
Ear Fullness
One of the main reasons why TMJ can lead to a feeling of ear fullness is due to the close proximity of the temporomandibular joint to the ear. The TMJ is located just in front of the ear, and the two structures are closely connected anatomically.When the TMJ becomes inflamed or misaligned, it can put pressure on the nearby ear canal, causing a sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear.
This is often described as a “clogged” or “plugged” feeling, similar to what you might experience when you have a cold or sinus infection.Additionally, the muscles that control the movement of the jaw are also connected to the muscles that control the Eustachian tube, which is responsible for regulating the pressure in the middle ear. When these muscles become tense or irritated due to TMJ, it can disrupt the normal functioning of the Eustachian tube, leading to a feeling of ear fullness.
Dizziness
Dizziness is another common symptom experienced by people with TMJ, and it can be caused by a few different factors.First, the inflammation and muscle tension associated with TMJ can affect the inner ear, which is responsible for maintaining balance and equilibrium. The inner ear contains delicate structures that are sensitive to changes in pressure and movement, and the proximity of the TMJ to these structures means that TMJ-related inflammation can disrupt their normal functioning.
Additionally, the ear fullness and pressure that often accompanies TMJ can also contribute to feelings of dizziness or vertigo. When the pressure in the ear is uneven or fluctuating, it can disrupt the inner ear’s ability to accurately sense the body’s position and movements, leading to a sensation of dizziness or imbalance.
Finally, some research has suggested that the pain and muscle tension associated with TMJ can also trigger reflexive responses in the body that can contribute to dizziness. For example, the pain and muscle spasms in the jaw and neck area can lead to changes in blood flow or nerve signals that can affect the inner ear and balance system.
Diagnosing and Treating TMJ-Related Ear Fullness and Dizziness
If you’re experiencing ear fullness, dizziness, or other symptoms that you suspect may be related to TMJ, it’s important to seek medical attention from a qualified healthcare provider. They can perform a thorough evaluation and help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing the connection between TMJ and ear fullness or dizziness typically involves a combination of:
- Medical history and physical examination: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries or trauma to the jaw or head. They will also perform a physical examination, checking for tenderness, clicking, or other signs of TMJ.
- Imaging tests: Your provider may order imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, to get a closer look at the structure and alignment of the TMJ.
- Hearing and balance tests: Your provider may also refer you to an audiologist or vestibular specialist for tests to evaluate your hearing and balance function, which can help determine if the ear fullness and dizziness are related to inner ear or balance issues.
Treatment
Once a diagnosis of TMJ-related ear fullness and dizziness has been made, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a treatment plan. The specific treatment approach will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the underlying cause of your TMJ, but may include:
Conservative Treatments
- Jaw exercises and physical therapy: Exercises and physical therapy techniques can help strengthen and stretch the muscles around the TMJ, reducing pain and improving range of motion.
- Oral appliances: Custom-made mouth guards or splints can be worn at night to prevent teeth grinding and clenching, which can help alleviate TMJ symptoms.
- Medication: Over-the-counter or prescription anti-inflammatory medications, muscle relaxants, or pain relievers may be used to manage pain and inflammation associated with TMJ.
- Stress management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help reduce the stress and anxiety that can exacerbate TMJ symptoms.
More Invasive Treatments
- Injections: In some cases, your provider may recommend injections of corticosteroids or Botox into the TMJ to reduce inflammation and muscle tension.
- Surgery: In severe or persistent cases of TMJ, surgery may be recommended to repair or realign the joint. This is typically considered a last resort option.
It’s important to note that the treatment of TMJ-related ear fullness and dizziness may require a multi-disciplinary approach, involving collaboration between your dentist, primary care provider, physical therapist, and potentially other specialists, such as an audiologist or neurologist.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing ear fullness, dizziness, or other unexplained symptoms, it’s important to consider the possibility of TMJ as a contributing factor. By working closely with your healthcare team to diagnose and treat the underlying TMJ condition, you can find relief from these troublesome symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
Remember, the key to managing TMJ-related ear fullness and dizziness is to address the root cause of the problem – the TMJ itself. With the right treatment approach, you can regain control of your symptoms and get back to living your best life.